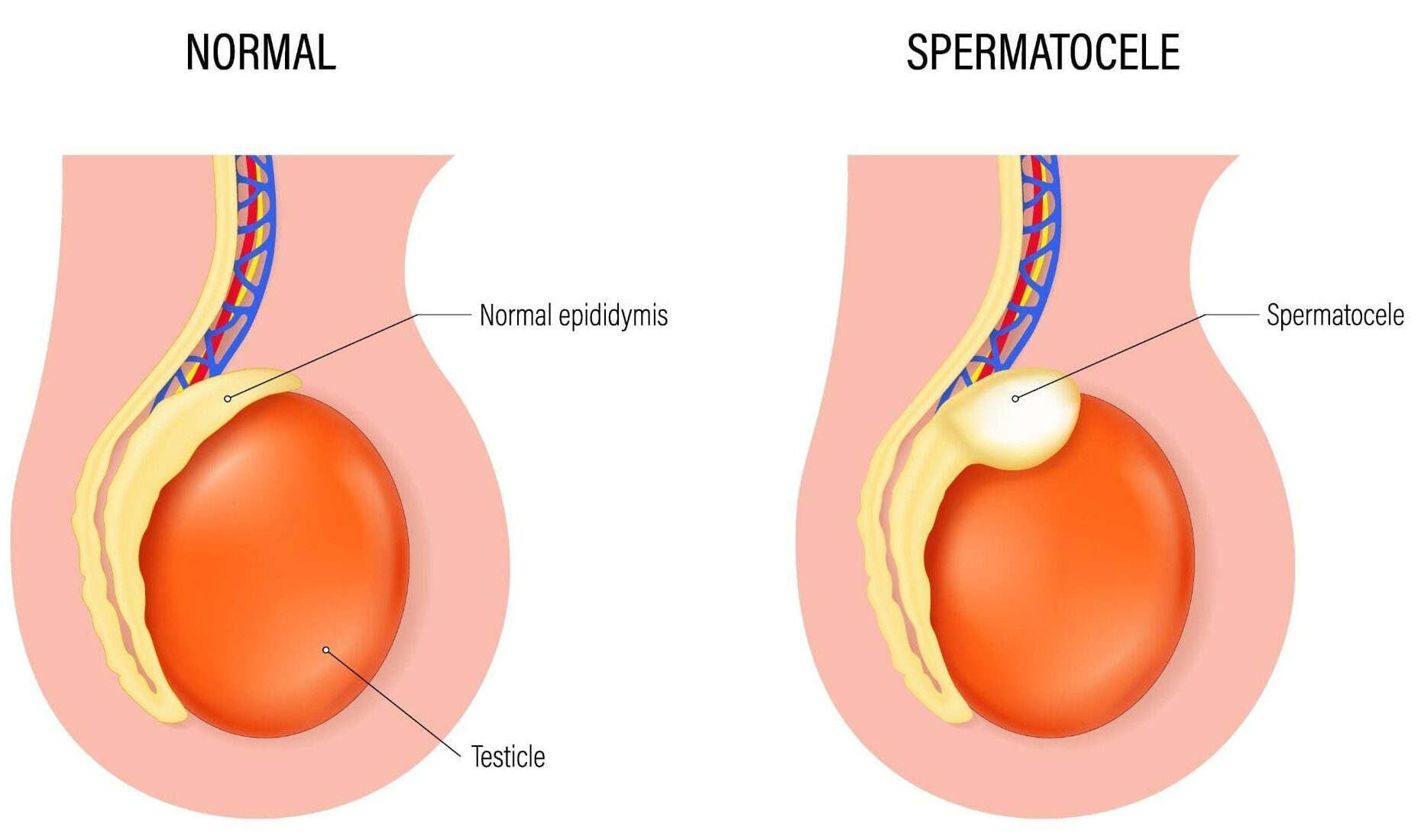
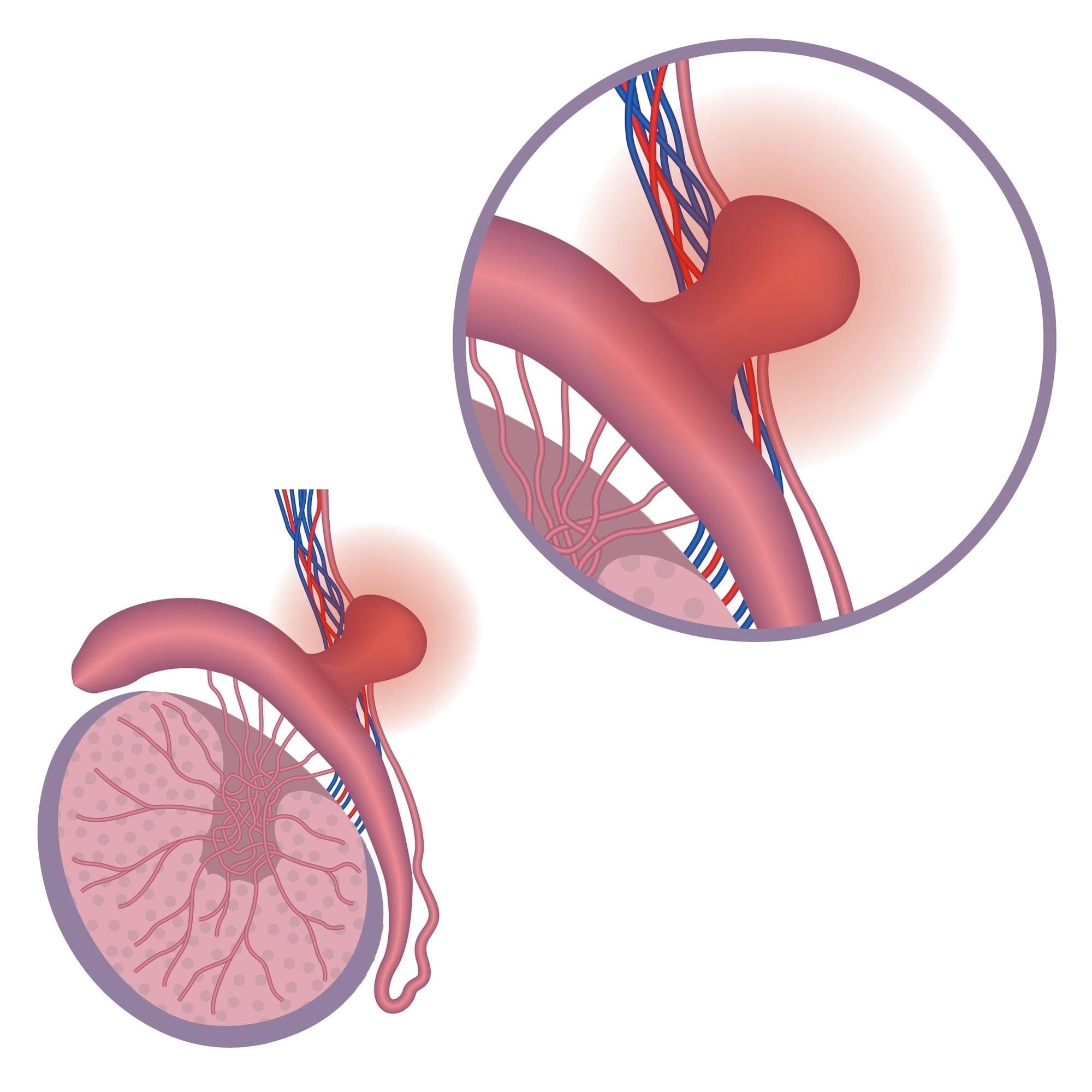
- UPNT clinics will open at a delayed time at 10 AM on 11/11-23 Secondary to the ice storm. we will continue to update on the website as conditions may change.
- UPNT clinics will open at a delayed time at 10 AM on 11/11-23 Secondary to the ice storm. we will continue to update on the website as conditions may change.
- UPNT clinics will open at a delayed time at 10 AM on 11/11-23 Secondary to the ice storm. we will continue to update on the website as conditions may change.
Menu